Latest Publications
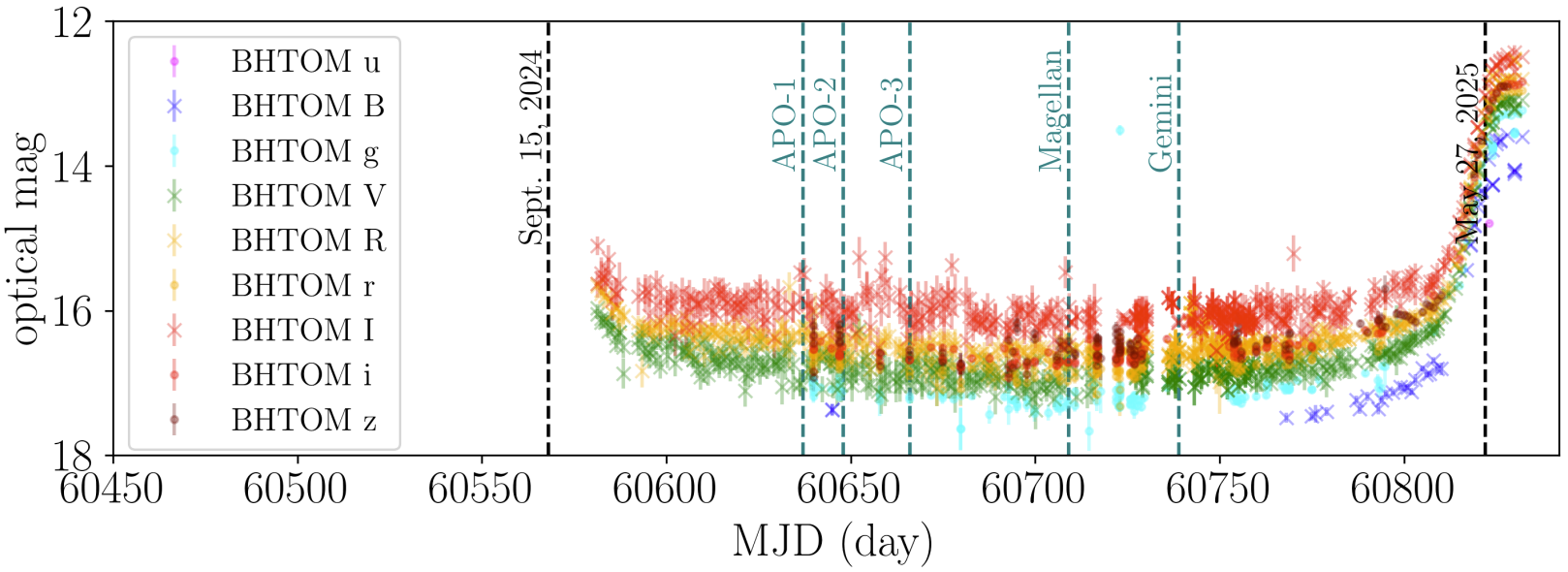
ASASSN-24fw: Candidate Gas-rich Circumsecondary Disk Occultation of a Main-sequence Star
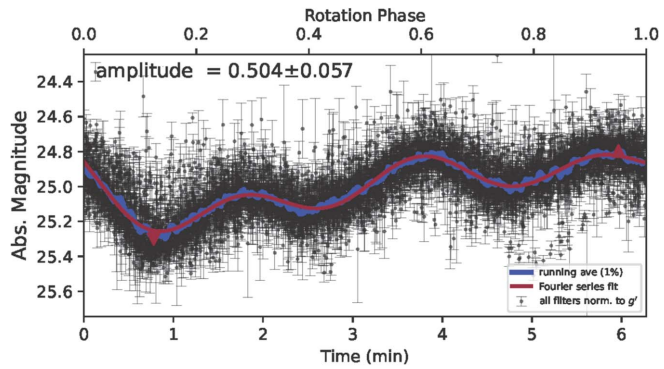
Dusty disks around planetary and substellar companions in outer reaches of exoplanetary systems can be detected as long-lasting occultations, provided the observer is close to the secondary's orbital plane. Here we report optical spectroscopy with KOSMOS (Apache Point Observatory), MagE (Magellan), and GHOST (Gemini-S) of ASASSN-24fw (Gaia 07:05:18.97+06:12:19.4), a 4 mag dimming event of a main-sequence star which lasted 8.5 months. We discover multiple low-ionization metal emission lines with velocity dispersion ≲ 10 km s−1 blueshifted by 27 km s−1 with respect to the star, as well as kinematically complex Na D absorption.
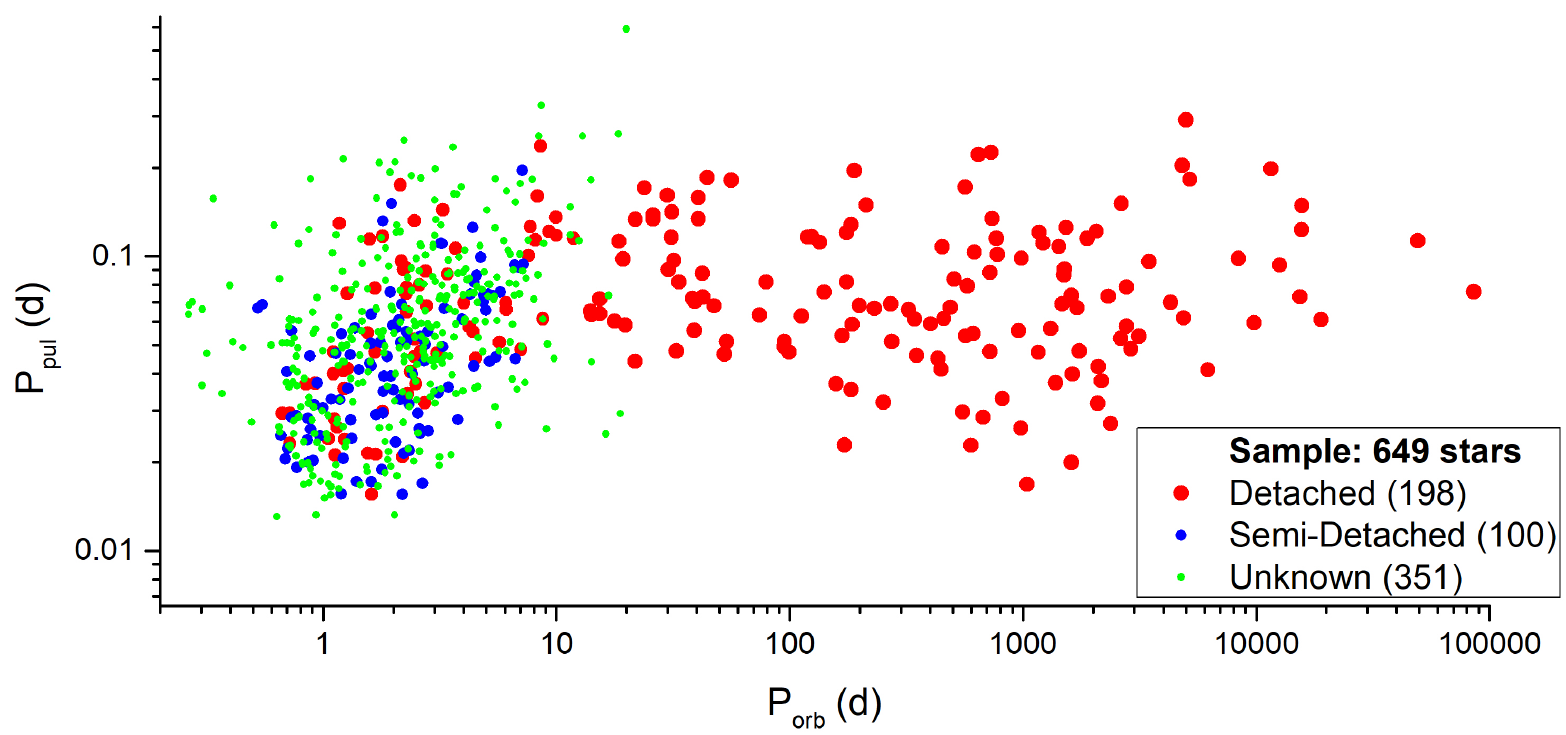
A catalogue of δ Sct pulsators in binary systems in 2024
The updated catalogue of δ Sct stars in binary systems as well as their statistical properties are presented. Thanks to the Kepler, K2 and TESS space missions, this version of the catalogue contains more than 1000 δ Sct pulsators in binaries. The sample is divided according to the Roche Geometry of the binary systems in order to check for any systematic differences in the pulsators' evolution due to the proximity of the companion star. Statistics, demographics, and distributions of these pulsating stars within the H-R and mass-radius diagrams are provided. We notice that the absolute parameters have been accurately determined for only approximately 10% of the whole sample. Additionally, updated correlations between pulsation and orbital periods and evolutionary status are presented. This work aims to motivate the researchers for systematic analyses of such objects in order to increase the sample of systems with well known physical properties.
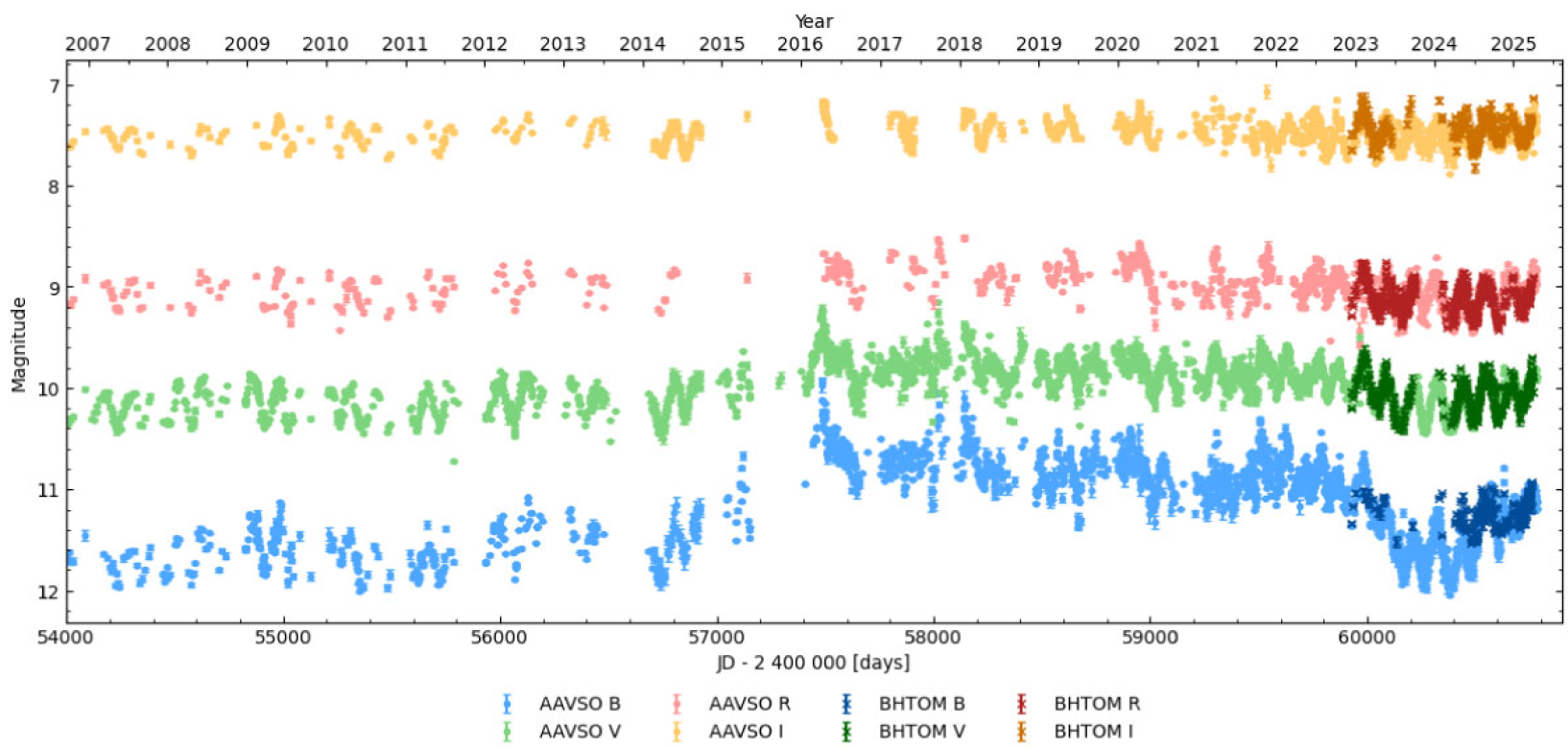
Is the symbiotic recurrent nova T CrB late? Recent photometric evolution and comparison with past pre-outburst behaviour
T CrB is a symbiotic recurrent nova that last erupted in 1946. Given its recurrence time-scale of approximately 80 yr, the next outburst is eagerly anticipated by the astronomical community. In this work, we analyse the optical light curves of T CrB, comparing recent photometric evolution with historical data to evaluate potential predictive indicators of no va eruptions. Although the 'superactive' phases preceding both the 1946 and anticipated eruptions are strikingly similar, the subsequent photometric behaviour differs. We find that the decline in brightness observed in 2023, interpreted by some as a 'pre-eruption dip', deviates from the deep minimum recorded prior to the 1946 event and does not reliably predict the eruption timing. Recent photometric and spectroscopic observations indicate that the system is returning to a high-accretion state. Given this, an eruption may be imminent, even without distinct precursors. While the next eruption of T CrB will be a major scientific event, its expected peak brightness of V ∼2 mag highlights the importance of setting realistic public expectations for what will be a visually modest, yet astrophysically very significant, celestial event.
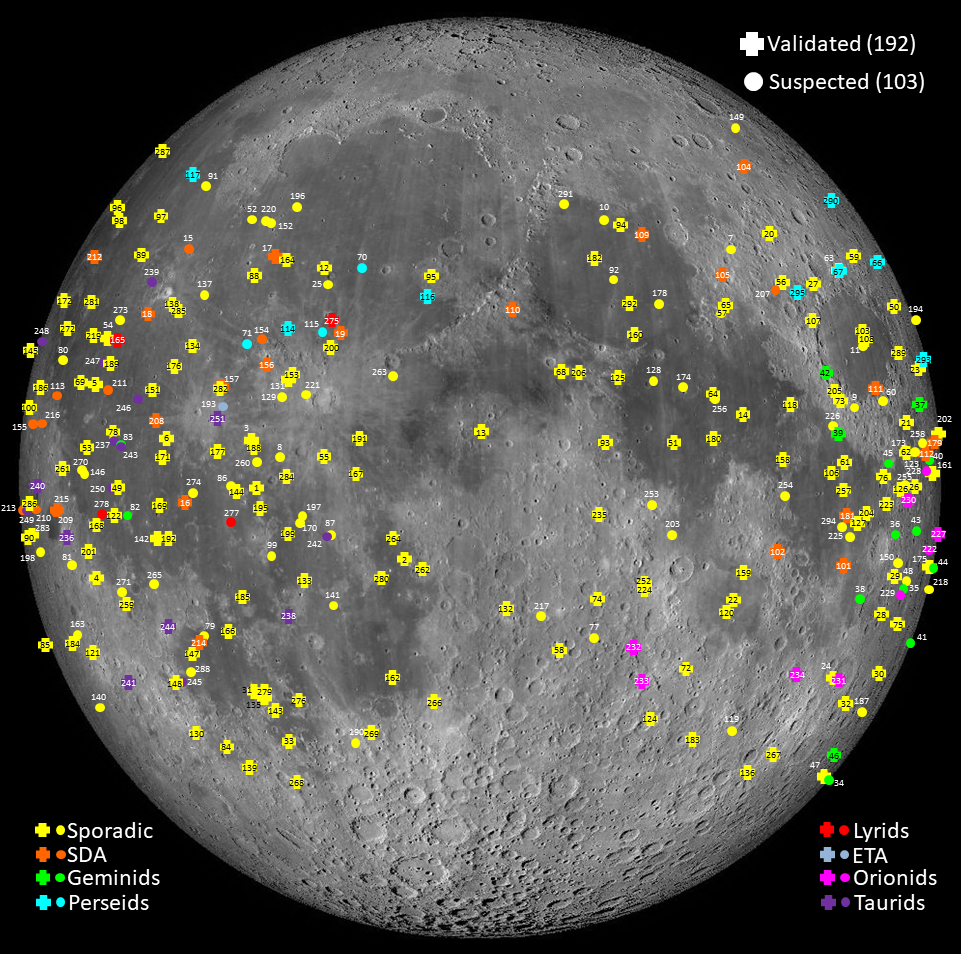
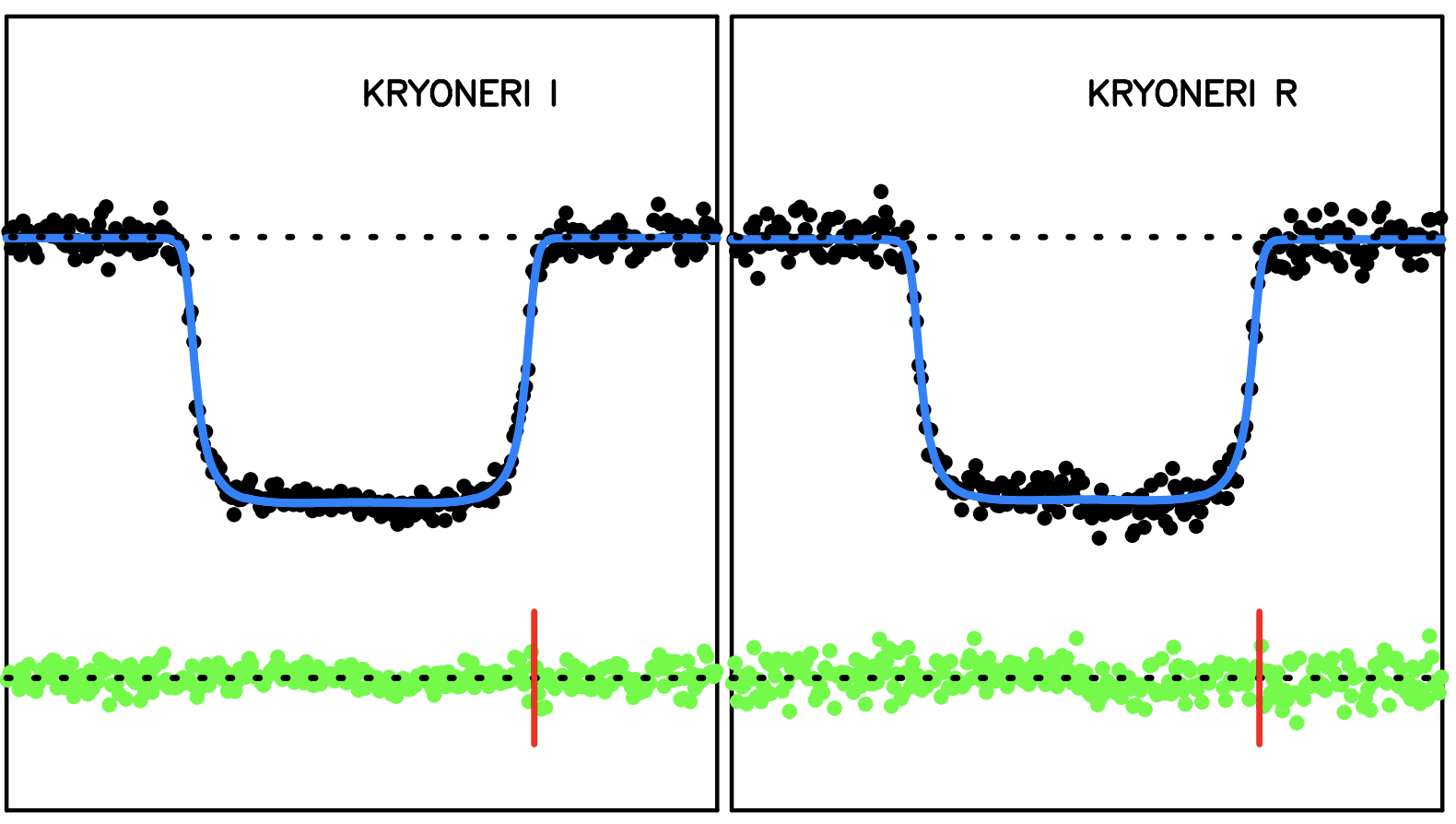
NELIOTA: New results and updated statistics after 6.5 years of lunar impact flashes monitoring
We present results of the Near-Earth objects Lunar Impacts and Optical TrAnsients (NELIOTA) campaign for lunar impact flashes observed with the 1.2 m Kryoneri telescope. From August 2019 to August 2023, we report 113 validated and 70 suspected flashes. For the validated flashes, we calculate the physical parameters (masses, radii) of the corresponding projectiles, the temperatures developed during the impacts, and the expected crater sizes...
2023 DZ2 Planetary Defense Campaign
We present the results of a fourth planetary defense exercise, focused this time on the small near-Earth asteroid (NEA) 2023 DZ2 and conducted during its close approach to the Earth in 2023 March. The International Asteroid Warning Network (IAWN), with support from NASA's Planetary Defense Coordination Office (PDCO), has been coordinating planetary defense observational campaigns since 2017 to test the operational readiness of the global planetary defense capabilities. The last campaign focused on the NEA Apophis, and an outcome of that exercise was the need for a short burst campaign to replicate a real-life near-Earth object impact hazard scenario. The goal of the 2023 DZ2 campaign was to characterize the small NEA as a potential impactor and exercise the planetary defense system including observations, hypothetical risk assessment and risk prediction, and hazard communication with a short notice of just 24 hr. The entire campaign lasted about 10 days. The campaign team ...
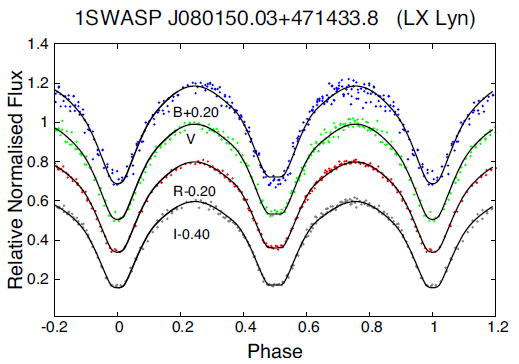
CoBiToM Project — II: Evolution of contact binary systems close to the orbital period cut-off
Ultra-short orbital period contact binaries (Porb
Constraints on the structure and seasonal variations of Triton’s atmosphere from the 5 October 2017 stellar occultation and previous observations
A stellar occultation by Neptune's main satellite, Triton, was observed on 5 October 2017 from Europe, North Africa, and the USA. We derived 90 light curves from this event, 42 of which yielded a central flash detection. We aimed at constraining Triton's atmospheric structure and the seasonal variations of its atmospheric pressure since the Voyager 2 epoch (1989). We also derived the shape of the lower atmosphere from central flash analysis.